Finding Corners
Basic Idea
"corner": significant change in all directions with small shift
Key Property
In the region around a corner, image gradient has two or more dominant directions.
Harris Corners
Start with an image , the change in appearance after shifting that image some (small) amount (), over some window function , is represented by an error function:
Window Function
A Gaussian Filter that will weigh pixels near the center of the window appropriately.
Taylor Expansion
We want a large error for a small shift that indicates a corner-like region. We use Taylor expansions .
In 2D, the 2nd order Taylor Expansion about (0, 0):
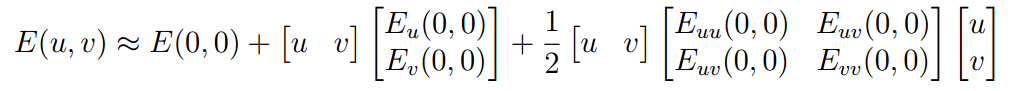
Simplify: Where M is a second moment matrix:
Properties of the Second Moment Matrix
The surface is locally approximated by a quadratic form.
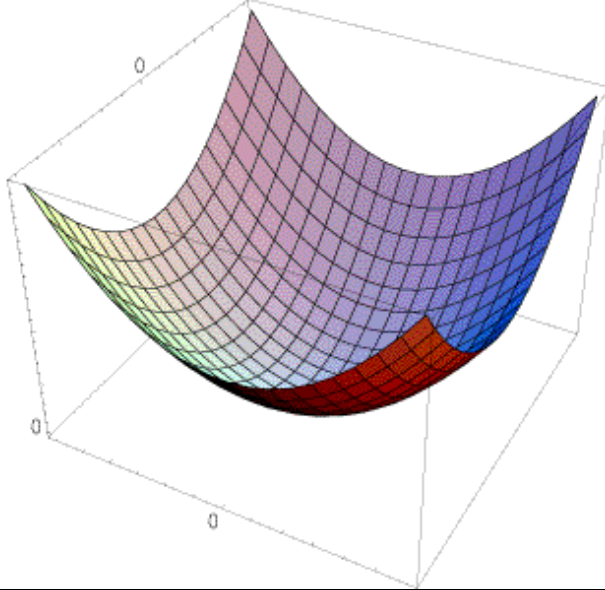
Consider a constant "slice" of , this is the equation of an ellipse.
Diagonalization of M: where s are the eigenvalues.
gives us the orientation of the ellipse and s give us the length of its major and minor axes.
Harris Response Function
Empirically,
The classification breakdown:
Harris Detector Algorithm
1. Compute Gaussian derivatives at each pixel
2. Compute second moment matrix M in a Gaussian window around each pixel
3. Compute corner response function R
4. Threshold R
5. Find local maxima of response function (nonmaximum suppression)